Home
Wecome to the final unit of your Level 3 qualification - I would like to see, in the next two weeks, a draft of your final assignment so I can see you are on the right track and to basically get you all started ;o) and your diaries with 24+ entries. Please arrange a tutorial if you can't get started.
Systems Application - Servers
The Networking Operating System - NOS
There are two basic types of networks as illustrated in the following table
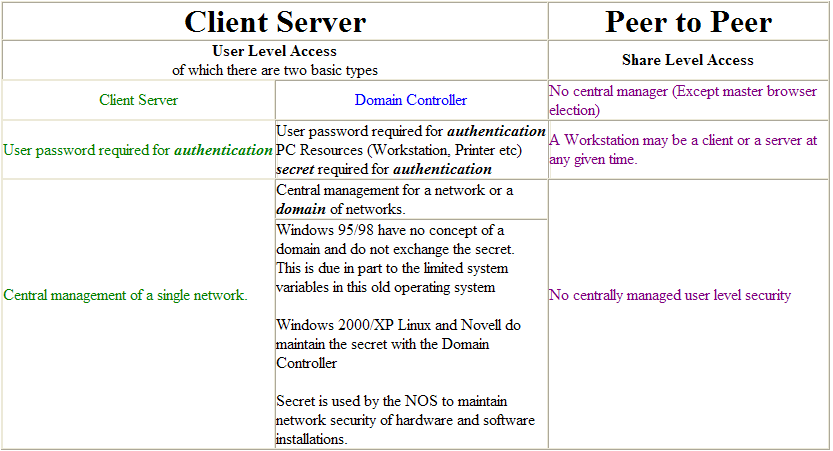
A client server network (That is not a Domain) is typically a single LAN with services like DHCP, DNS, HTTP, NTP, FTP, SMTP, POP3, printer and file sharing
A Domain is a network, or a collection of networks that are managed in a hierarchical name structure. This structure resembles the roots of a tree how they branch down. For this reason the top level of a domain structure is called The Root.
www.huddcoll.ac.uk is a domain
The top level domain is always the last part of the domain name, in this case it is the UK domain. AC is a child domain of UK, HUDDCOLL is known as the child of the AC domain and the grandchild of the UK domain. Finally WWW is the standard name for the web server in a domain, which is simply a server which serves requests for web pages to the Internet.
Domains within an organisations network follow the same concept. MS Windows and Novel refer to these as Trees and Forests
In our room we have a Linux server running as a Domain Controller. Its name is linsrvr but it also has the alias www The domain is named slwt and belongs to the .co.uk top level domains (This would have to be registered with Nominet) This server runs the service HTTP so when you type http://www.slwt.co.uk you get the website hosted on the server!
A Domain Controller (DC), which is simply a server with the appropriate software, can manage other Domain Controllers. In this role it is known as a Primary Domain Controller (PDC). In each of the PCs belonging to a domain there has been an exchange of a secret, and a trust developed between them and the DC.
Users set up on the PDC can use the network in every location across the organisation because each local DC trusts the PDC and will check with it for authentication. Users set up on each DC can use the network within that domain only. This can be completely managed by the network administrator.

A domain does not refer to a single location or specific type of network configuration. The computers in a domain can share physical proximity on a small LAN or they can be located in different parts of the world. As long as they can communicate, their physical position is irrelevant.
The benefits of a domain are
- Centralised Administration - Management of the entire domain can be done with access to one database.
- Single Logon Process - Access to network resources can be granted through a single logon.
- Scalability - Very large networks can be created.
Authentication and Authorisation
Authentication
This is the proof. 'you are who you say you are'. For users in a network, this is determined by the validation of a user name and a corresponding password. For PC's in a domain it is also the validation of a secret key shared with the domain controller.
This is the first level of security for people who have access to the network.
Authorisation
These are the permissions that a machine or a user has once they have been authenticated. This takes the form of Group Policy and Resource Permissions set by the network's administrator.
Further Reading
Interview preparationTypical Interview Questions
Network Engineer Questions
First IT Jobs
