Home
Understanding how secure is a password.
Lockdown.co.ukLabmice
Network administrators use varying methods to maintain password security. Most commonly is the requirement for a user to regularly change their password. To prevent use of common words, or just adding 1s to their passwords, many administrators apply rules that prevent passwords where more than two letters are in the same position as the old password. Unfortunately this sometimes leads to users keeping their passwords stuck to their monitors, which obviously defeats the purpose and requires enforcing network security.
In networking operating systems terms explain vertical and horizontal scalability.
Vertical scalability
This refers to improving network resources by adding additional processing power, usually in the form of modular rack mounted systems such as those developed by Sum Microsystems and Intel.
Horizontal scalability
This refers to improving network resources by adding addition work stations, switches and routers. Generally anything that spreads the networking resources.
What is legacy in computing terms.
Legacy is any device, port or socket that is considered old technology that needs to remain in operation due to another component still dependant on them. Examples of legacy items are com ports, parallel ports, floppy drive, IDE, AGP and ISA sockets. Items considered as legacy will change as new technology is developed.
Becoming familiar with the Linux shell

Linux is managed by either a GUI shell or a Command Line shell. Much of the power use of a Linux machine is performed in the command line shell.
As in DOS a command is a single word without spaces typed at a prompt (#). E.g.cd Change directory ls List directory pwd Print Working Directory
Again as in DOS commands can be extended by using command line switches which always follow a command with a space.
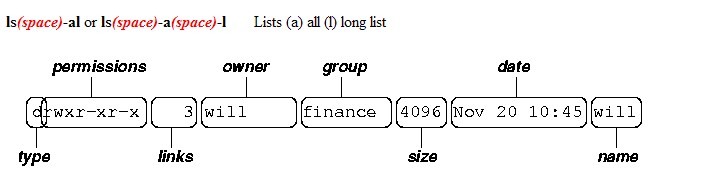
Every resource on a Linux machine has permissions which govern who can do what. There are three basic permissions; Read, Write and Execute. E.g. drwxrwxrwx

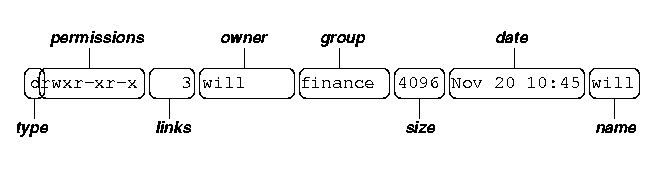
What are Will's permissions above?
What are the permissions for the group finance?
What are the permissions for the world?
Further Reading
Explanatory Notes to Special Educational Needs And Disability Act 2001Links to disability resources relating to PCs
Example of an organizations special needs accessibility.
Guidelines to Windows Accessibility settings.
Apple.com - Outline their accessibility features.
Linux - Outline their accessibility features.