Home

Write your own exam questions
Network Block Exercise Sheet
Network Diagnostics
Troubleshooting a network. Look for the simple things first! Is it plugged in? Etc.
Some well written diagnostics articles for TCP/IP networks from Microsoft here and here.
Is there anything wrong with each of these four networks?
What is IPv6 and 6bone?
Wiki - IP Version 6 ExplainedNew IP addresses being developed by the IANA and partners to solve the problem of a critical shortage of globally unique IPv4 IP addresses.
128 Bit addresses (As opposed to IPv4 32 bit addresses) enough for every network able device in the world, whether that be a PC, phone or the refrigerator! Being tested and implemented on 6bone (IPv6 Backbone).
Current projects include digital medical imaging across the Pacific Rim where digital video is encapsulated in IPv6 and transmitted at 30fps over native IPv6 networks (SDSC, Abeline, SURFnet) between San Diego and Amsterdam. (PRAGMA PPT_3.7MB file)
Increased security, reliability, priority for streaming data.
Can be 'Tunneled' on an IPv4 network if the equipment has been upgraded to support this protocol. That is, packets of IPv6 carried in (encapsulated in) IPv4 packets.
IPv6 is for the convergence of digital information. Technologies like Mobile networks 3G and mms (Multimedia Stream with packet prioritisation see www.freefootball.org and the Nokia presentation below)
IPv6 does not require a subnet mask - There are more than enough numbers (range) to enable 1 network for every networkable device in the world currently and in the foreseen future!
WiFi - 802.11
WiFi is short for Wireless Fidelity
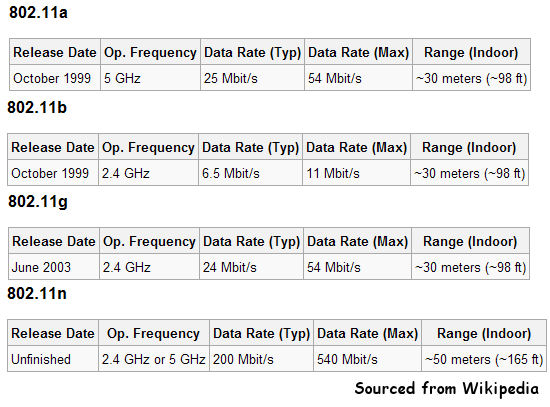
Wireless clients operate within an Ethernet LAN transparently, that is other clients do not identify them as being wireless.
With wireless being very congested with AM, FM, TV, Bluetooth and Microwave, WiFi works in a narrow bandwidth with 11 bands (A band being likened to a LAN). Networked clients in a LAN must operate on the same band, and other LANs close by must operate on a different band to avoid congestion.
Security is achieved by using either WEP, WPA or WPA2, which depending on the one chosen requires either a Pass Phrase, A 10 digit 64Bit Hex Key or a 26 digit 128 Bit Hex key.
Wireless clients can be Ad Hoc, which basically means they will connect with any network to which they are configured, or Infrastructure. Infrastructure means there is a dedicated Access Point to connect to, usually a device to bridge the connection to the wired LAN.
So called PreN wireless products have been on the market for the last 24 months or so (Note the date on the link and it still is not ratified) that have pre-empted the 802.11n standard and claim increased speed. Another product is MiMo, which is basically a technology that uses two channels at once. All very fine if you are not in a congested wireless neighborhood.
Further Reading
PDF document on Wireless NetworksNetworking articles
Bluetooth
Ad Hoc - How to